ilog-本地执行规则
前言
由于我们公司用到ilog规则引擎,于是记录一下如何在本地执行规则集.方便以后自己查找.
新建规则项目以及XOM项目
这两个项目是我写的一个小例子,用于演示一些基本操作.
项目结果如下:

新建规则
如果
'保单' 的被保险人 的年龄 小于 20
那么
'返回结果' . 添加返回结果( "被保险人年龄控制",不成立 ,"被保险人年龄小于20") ;
否则
'返回结果' . 添加返回结果( "被保险人年龄控制",成立 ,"被保险人年龄大于20") ;
这是一个被保险人年龄的判断规则.
发布到res进行测试
在将本地测试之前,我先发布到res进行测试.看看项目有没有什么问题.
-
新建RuleApp项目
-
右键规则项目 -> 新建 -> 其他
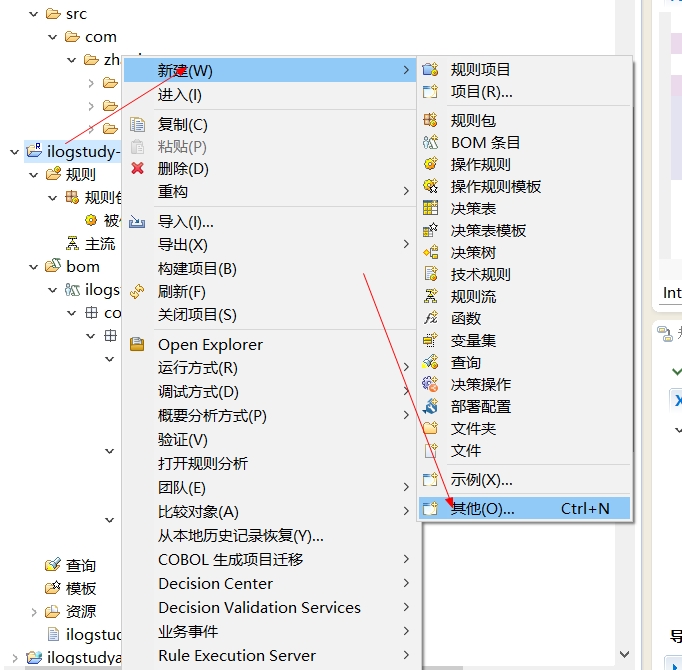
-
选择RuleApp项目
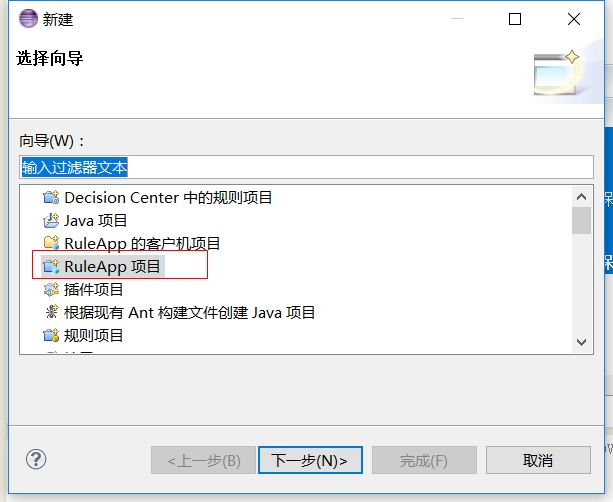
-
输入项目名称
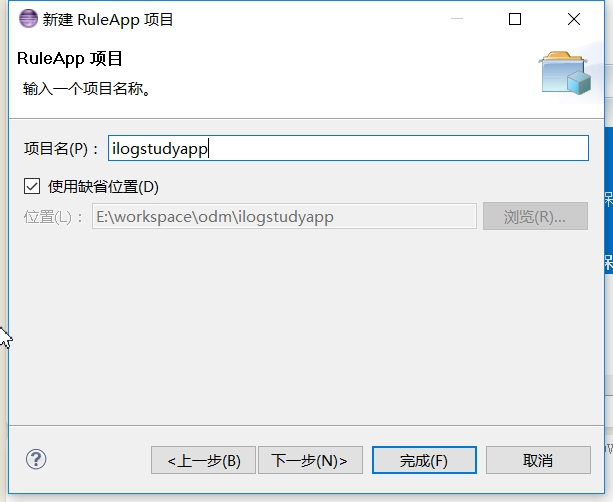
-
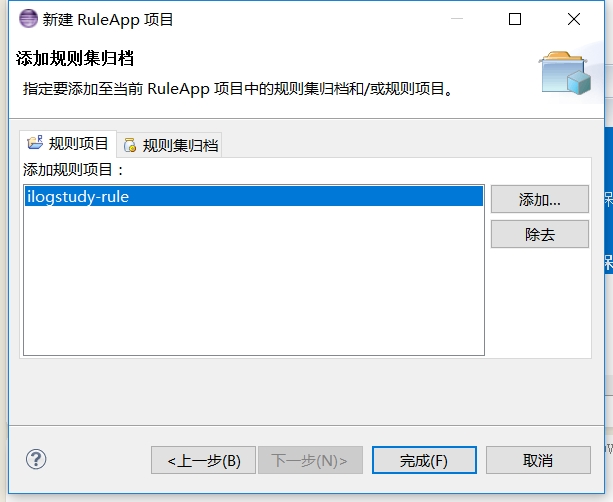
添加规则项目
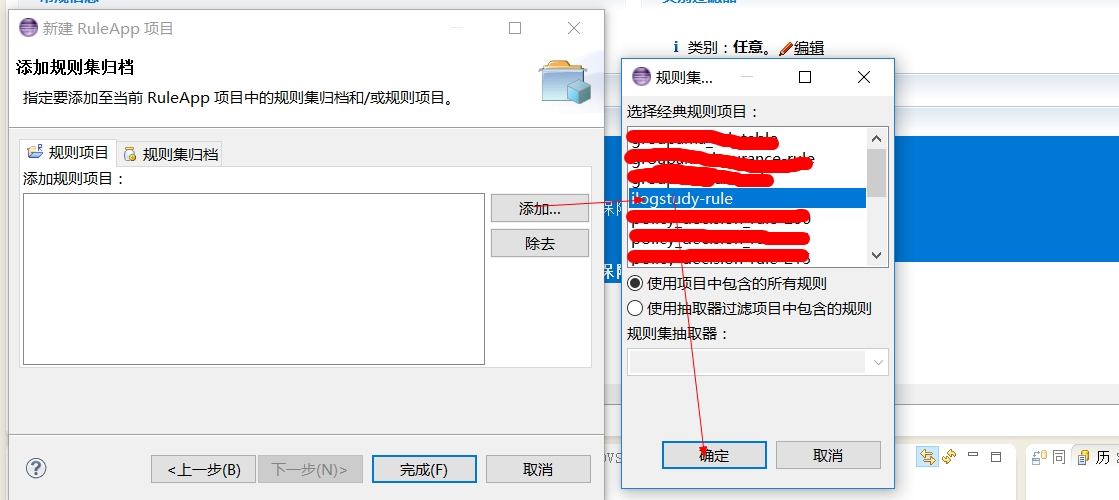
-
点击完成
-
-
将规则项目发布到res服务器
-
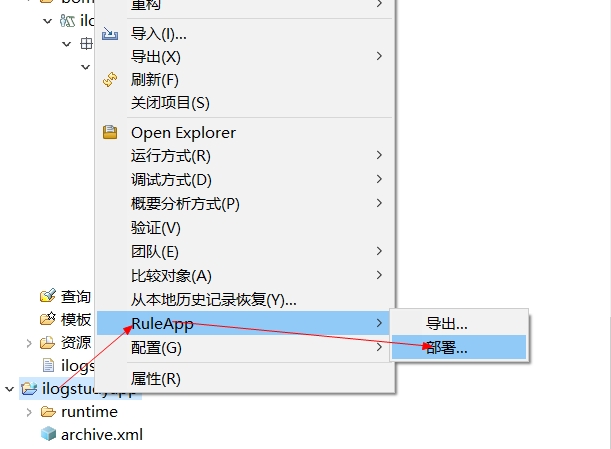
邮件RuleApp项目 -> RuleApp -> 部署
-
选择增量RuleApp主要版本

-
输入res服务器的地址,用户名以及密码,点击完成
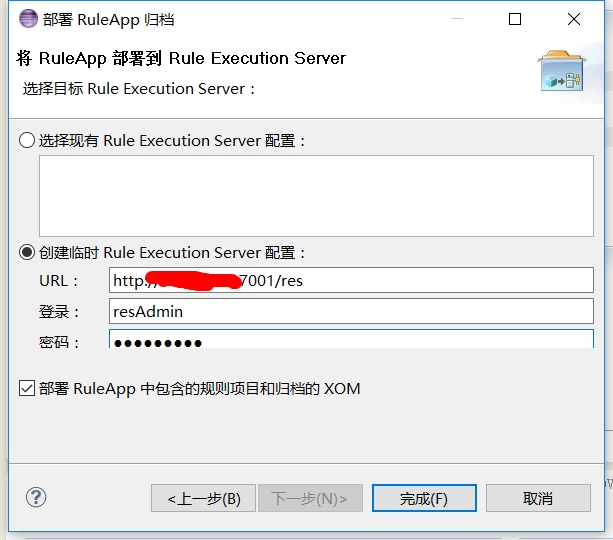
控制台看到如下结果表明已经成功部署上去了

-
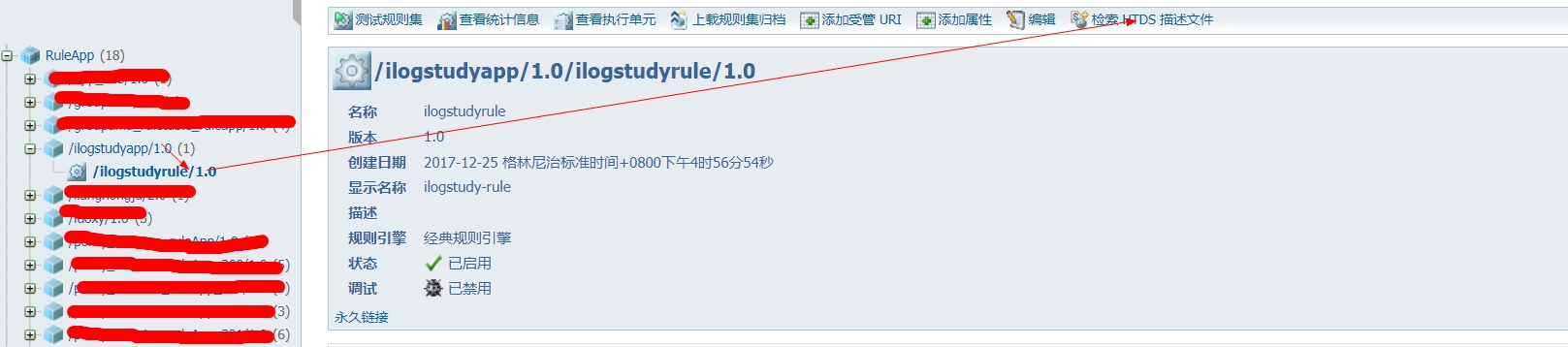
打开浏览器,访问res服务器,进入后点击资源管理器tab页,展开刚刚发布上去的项目,并点击规则集,然后点击右边的检索 HTDS 描述文件.
-
选择REST,并点击测试
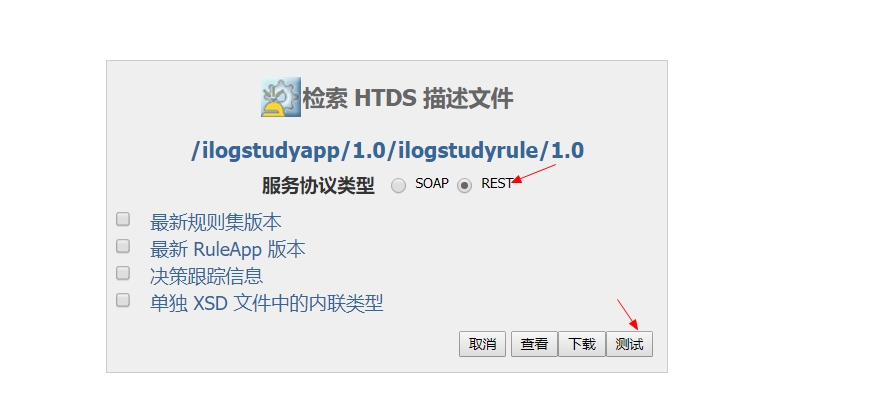
出现以下页面表示已经没问题了,如果进入这个页面报错,可能是你的项目有问题,再检查以下规则,以及规则流,jdk版本等是否符合规范.

-
-
测试
点击执行请求,返回以下结果

可以看到我们的项目返回了正确的结果,说明没有问题.那么,接下来,我们尝试在本地执行我们的规则.
本地测试
-
新建本地测试项目

-
将XOM项目中的代码考到测试项目中


-
新建lib文件夹,导入相关jar包,并把jar包引入到构建路径中

-
将规则集导出
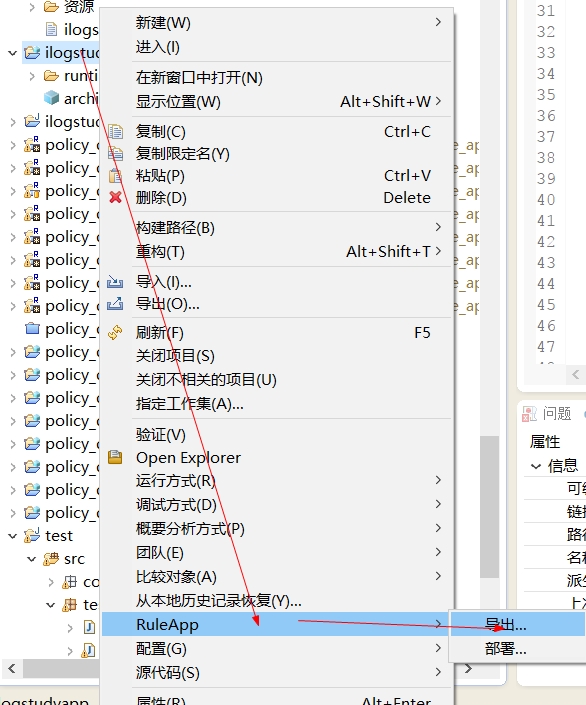
-
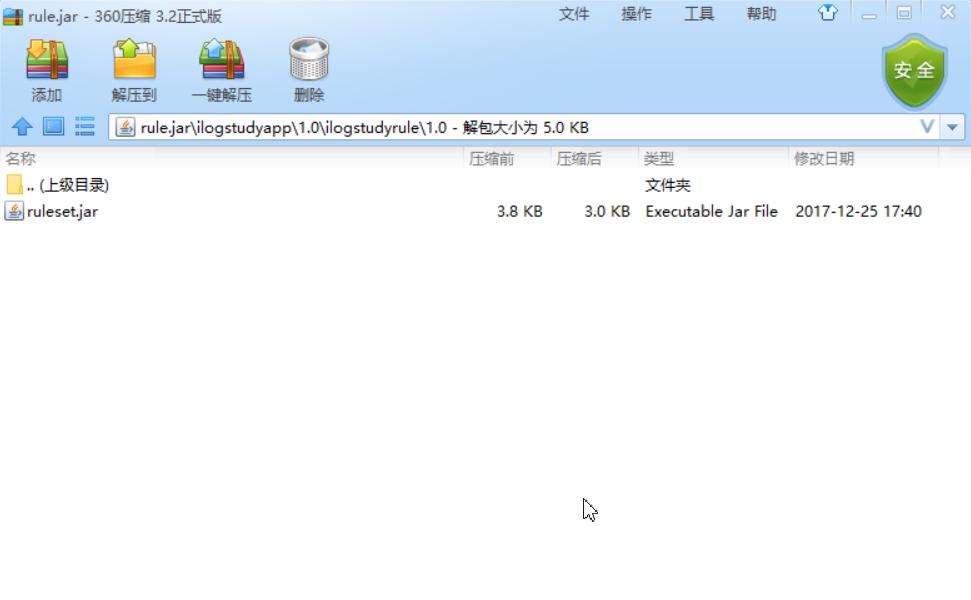
将导出后的jar包解压,复制其中的ruleset.jar到测试项目的lib下
6.新建test类,并键入一下代码进行测试
package test;
import ilog.rules.archive.IlrJarArchiveLoader;
import ilog.rules.engine.IlrContext;
import ilog.rules.engine.IlrParameterMap;
import ilog.rules.engine.IlrRuleset;
import ilog.rules.engine.IlrRulesetArchiveParser;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.util.jar.JarInputStream;
import com.zhaojun.bom.AppApplicant;
import com.zhaojun.bom.AppInsured;
import com.zhaojun.bom.Policy;
import com.zhaojun.result.UnderwriteResults;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
invokeIlrJar();
}
public static void invokeIlrJar() throws Exception {
// This class is a parser of ruleset archives. The archive is given as a
// stream. The parsing provides:
// a ruleset.
// a business reflect used in the case of a business ruleset archive.
// an execution reflect, used to create the provided ruleset.
IlrRulesetArchiveParser parser = new IlrRulesetArchiveParser();
// Creates an archive loader which relies on a jar stream.
IlrJarArchiveLoader ruleArchvieLoader = new IlrJarArchiveLoader(
new JarInputStream(new FileInputStream(
"E:\\workspace\\odm\\ilogstudytest\\lib\\ruleset.jar")));
// Parses the ruleset archive.
parser.parseArchive(ruleArchvieLoader);
// Get a ruleset issued from a ruleset archive parsing.
IlrRuleset rtsRuleSet = parser.getRuleset();
// IlrContext is the base class of all the execution contexts. Rules can
// be executed only within an execution context.
// In ILOG JRules, the rule engine is an instance of IlrContext, the
// rule engine is simply a Java object.
// An IlrContext instance is always attached to an IlrRuleset. If the
// context is created without a ruleset passed as an argument, it
// creates its own ruleset.
// An IlrContext instance contains all the methods required to control
// the rule engine. IlrRuleset is responsible for rule management,
// IlrContext is responsible for rule execution.
IlrContext context = new IlrContext();
context.setRuleset(rtsRuleSet);
// Implements a structure for storing parameter values to set or get
// from ruleset variables. Each parameter is stored with its name and
// its value.
IlrParameterMap paramMap = new IlrParameterMap();
Policy policy = new Policy();
AppApplicant appApplicant = new AppApplicant();
AppInsured appInsured = new AppInsured();
appApplicant.setName("jack");
appApplicant.setAge(18);
appApplicant.setGender(false);
policy.setAppApplicant(appApplicant);
appInsured.setName("jack");
appInsured.setAge(18);
appInsured.setGender(true);
policy.setAppInsured(appInsured);
// Store for the parameter "name" and its value "value".
paramMap.setParameter("policy", policy);
// Sets the values of the declared ruleset variables contained in the
// passed IlrParameterMap (defined either with the "in" or "inout"
// modifier).
context.setParameters(paramMap);
// Executes the ruleflow defined in the context's ruleset.
// Executes the task passed as the argument.
// context.execute(taskName);
context.execute();
// Gets the value of the ruleset parameter.
// Returns the values of the "out" ruleset variables (those defined
// either with the "inout" or "out" modifier).
// IlrParameterMap rpm = context.getReturnValues();
Object r = context.getParameterValue("result");
UnderwriteResults result =(UnderwriteResults)r;
if(result != null && result.getUnderwriteList() != null){
System.out.println(result.getUnderwriteList().get(0).getMessage());
}
// Disconnects all connected IlrTool.
context.disconnectTools();
// Called by Rule Studio to prepare a context for another execution.
context.reset();
}
}
7.运行测试类,见到以下输出结果.
被保险人年龄小于20
本地执行规则的好处就是执行速度比较快,而且能够对代码进行断点调试,方便查找bug.
本文地址是:ilog 本地执行规则 转载请注明原创地址。
参考博文:
Java调用ILOG两种形式备忘
ilog-本地执行规则
https://www.zhaojun.inkhttps://www.zhaojun.ink/archives/6